- Authority
- Relevance
Building authority in Google
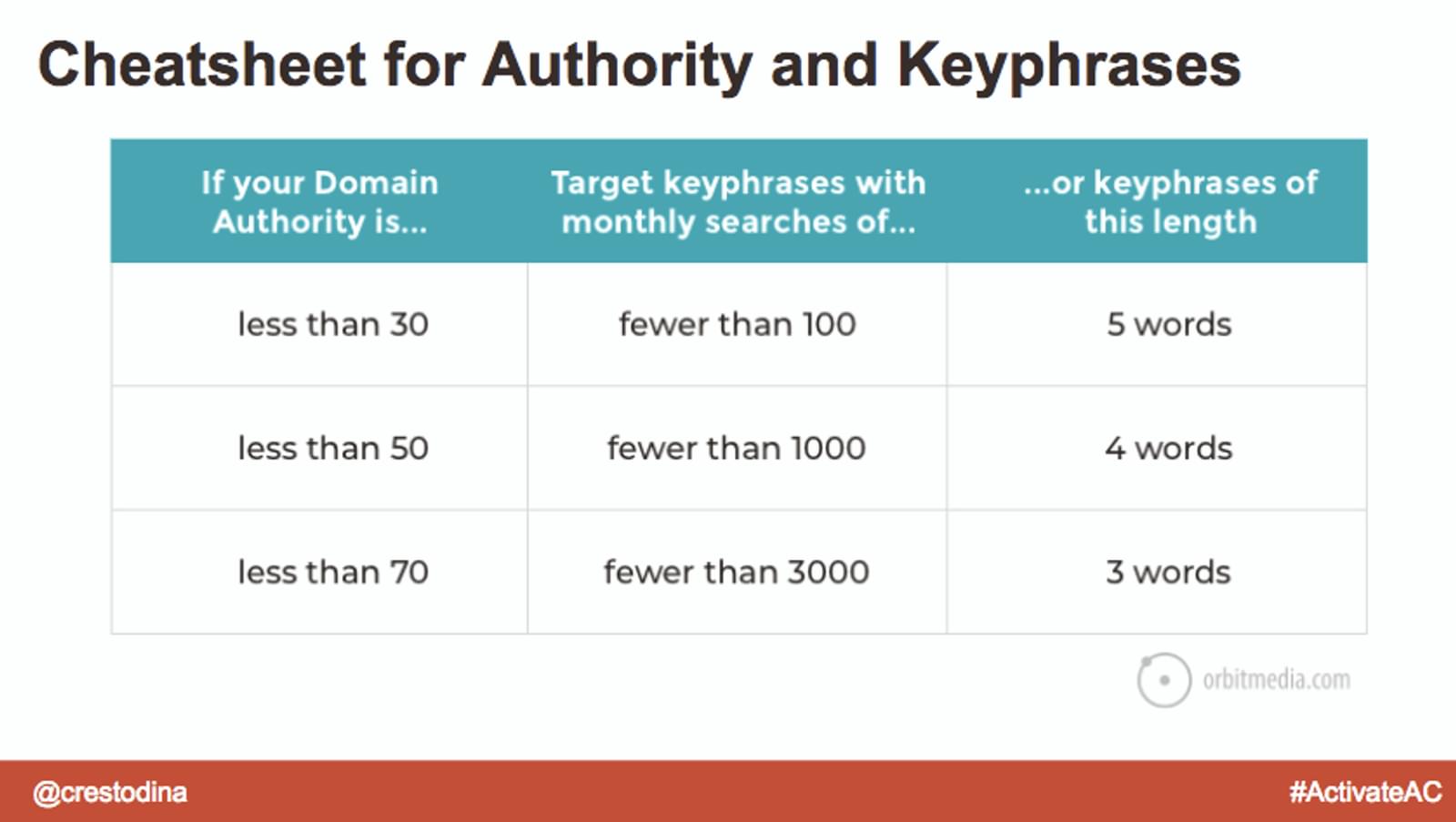
SEO ranking cheat sheet
How can you increase your Domain Authority? By building links. But how can you build links in a scalable way? Anyone who has ever sent link building emails knows that their success rate is pretty low.The answer? Make some friends!Guest post on other websites. Seek out content creators and include their quotes in your work—other creators are the people most likely to link to you...because they also create content!This approach to link building makes your blogging more effective as a whole.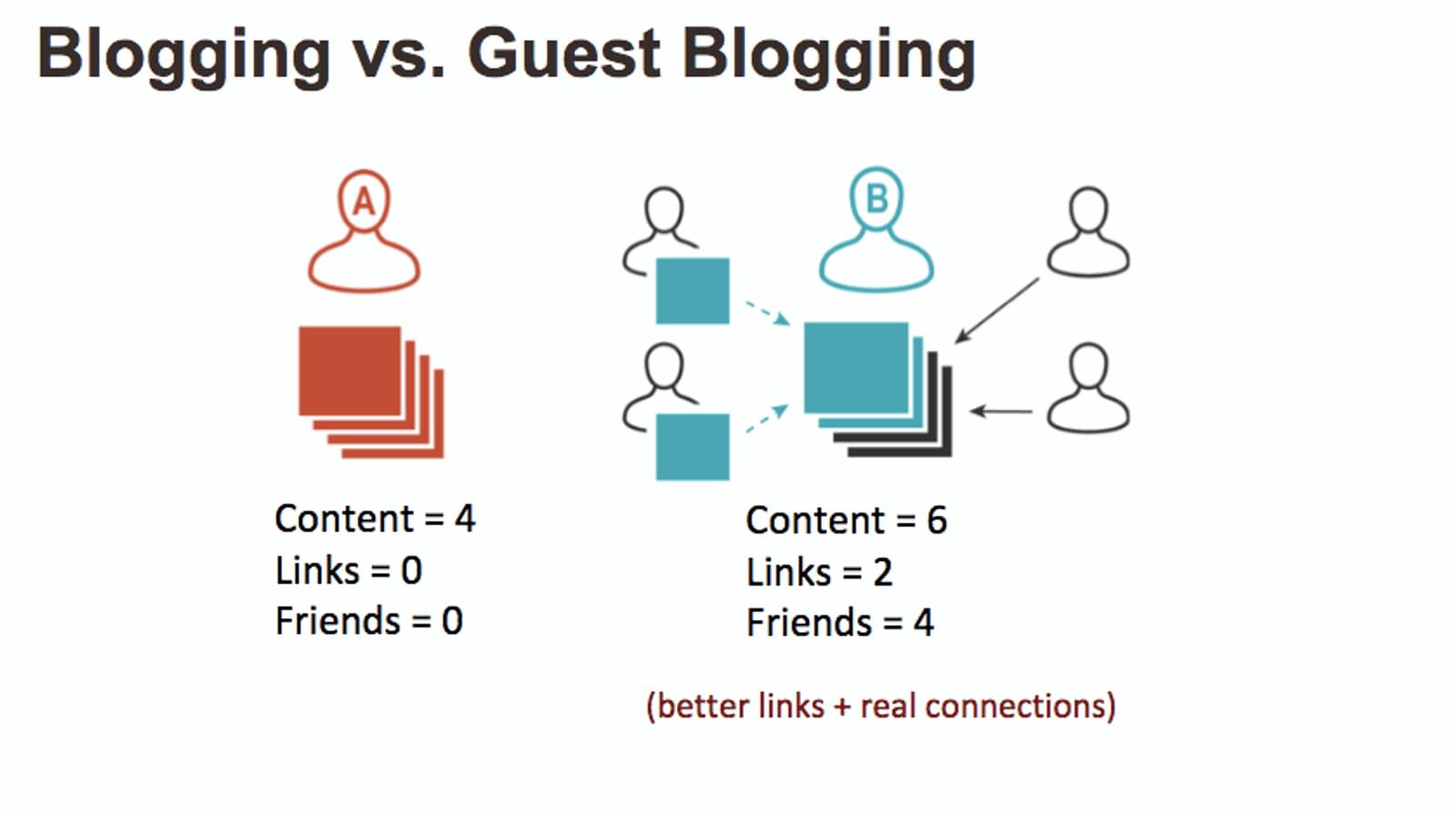
Social link building
Signaling relevance in Google
- High search volume
- Low competition
- Relevant to your business
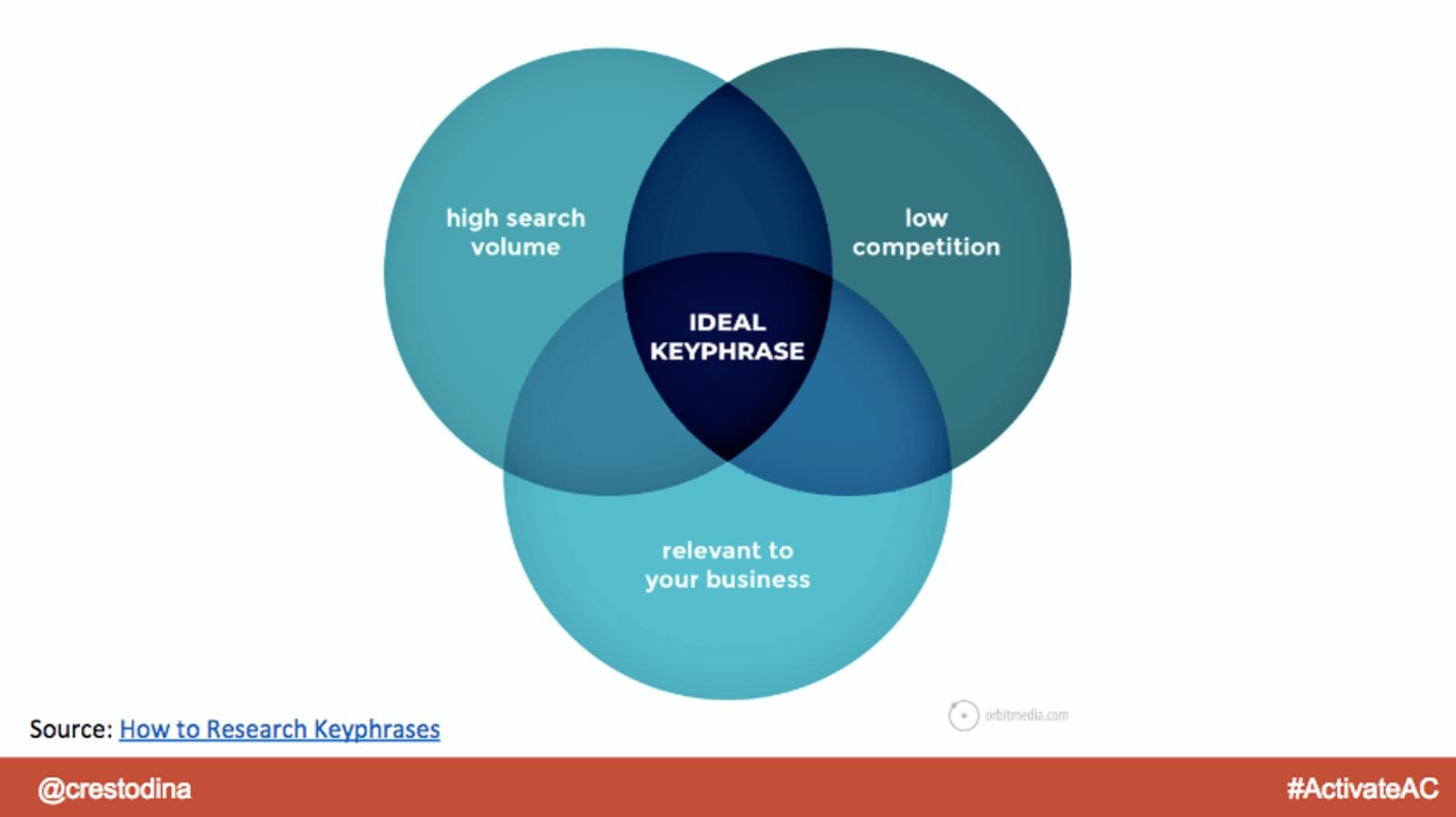
How to choose a keyword for your business
How do you find good keywords? There are a lot of keyword research tools, but Google Keyword Planner is free, and a good place to start.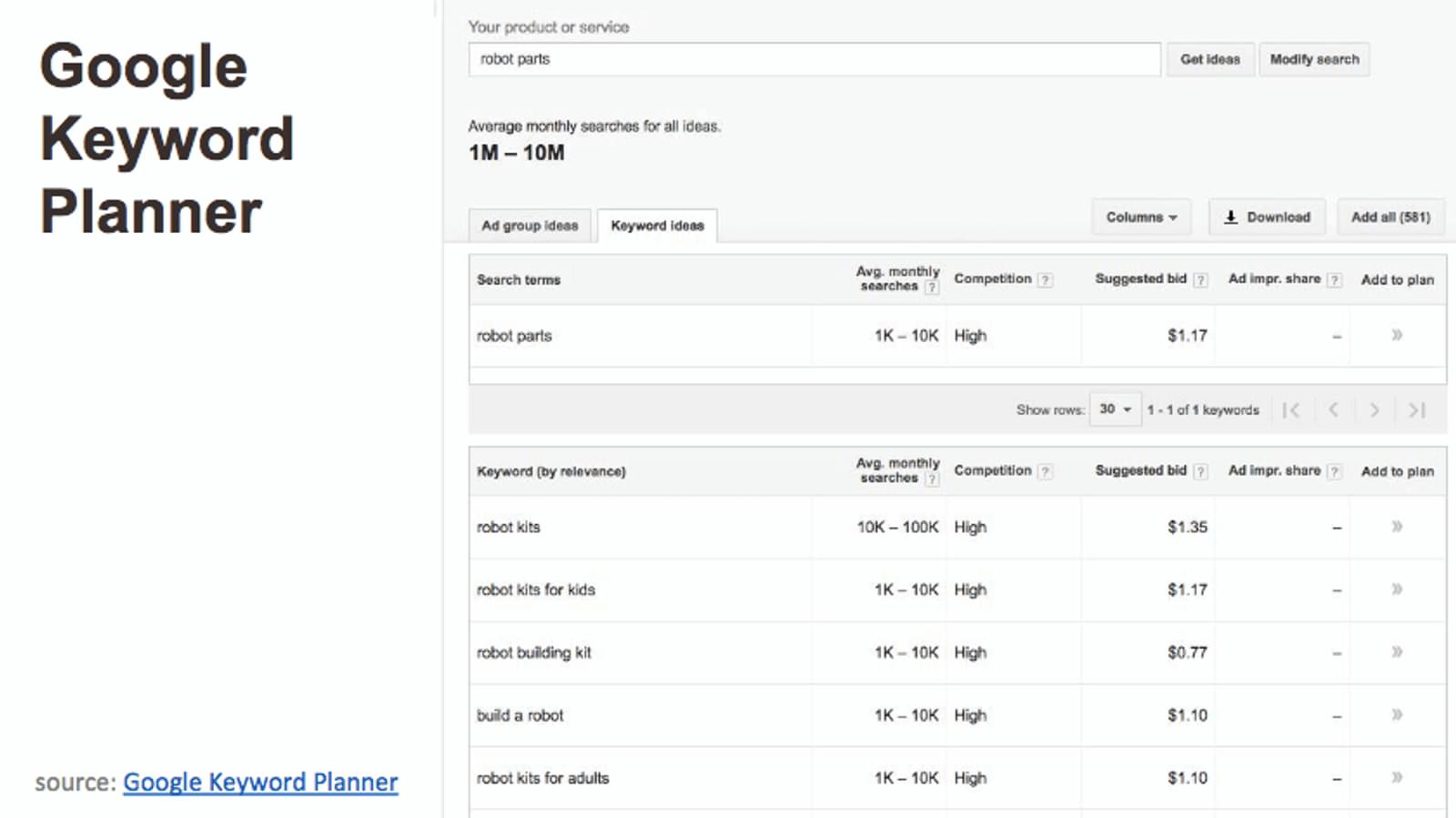
- Page title (<title>)
- <h1> header
- Body text (2-4 times every 500 words)
- Meta description
- Image alt text
- File names
- Meta keywords
Beyond simple keyword research: Target the broader topic
Google used to rank the pages that had the most keywords jammed inside them. Not anymore.
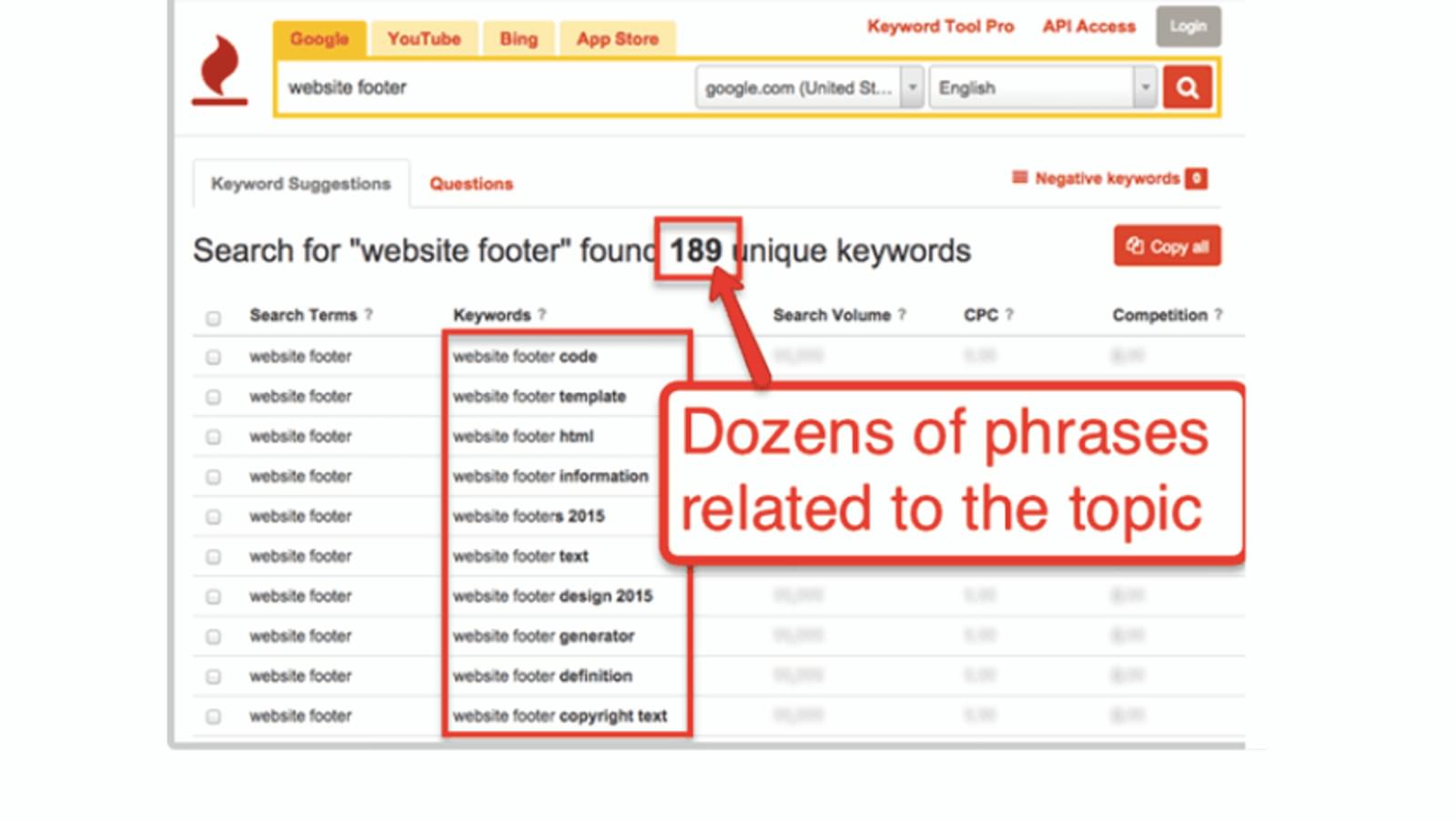
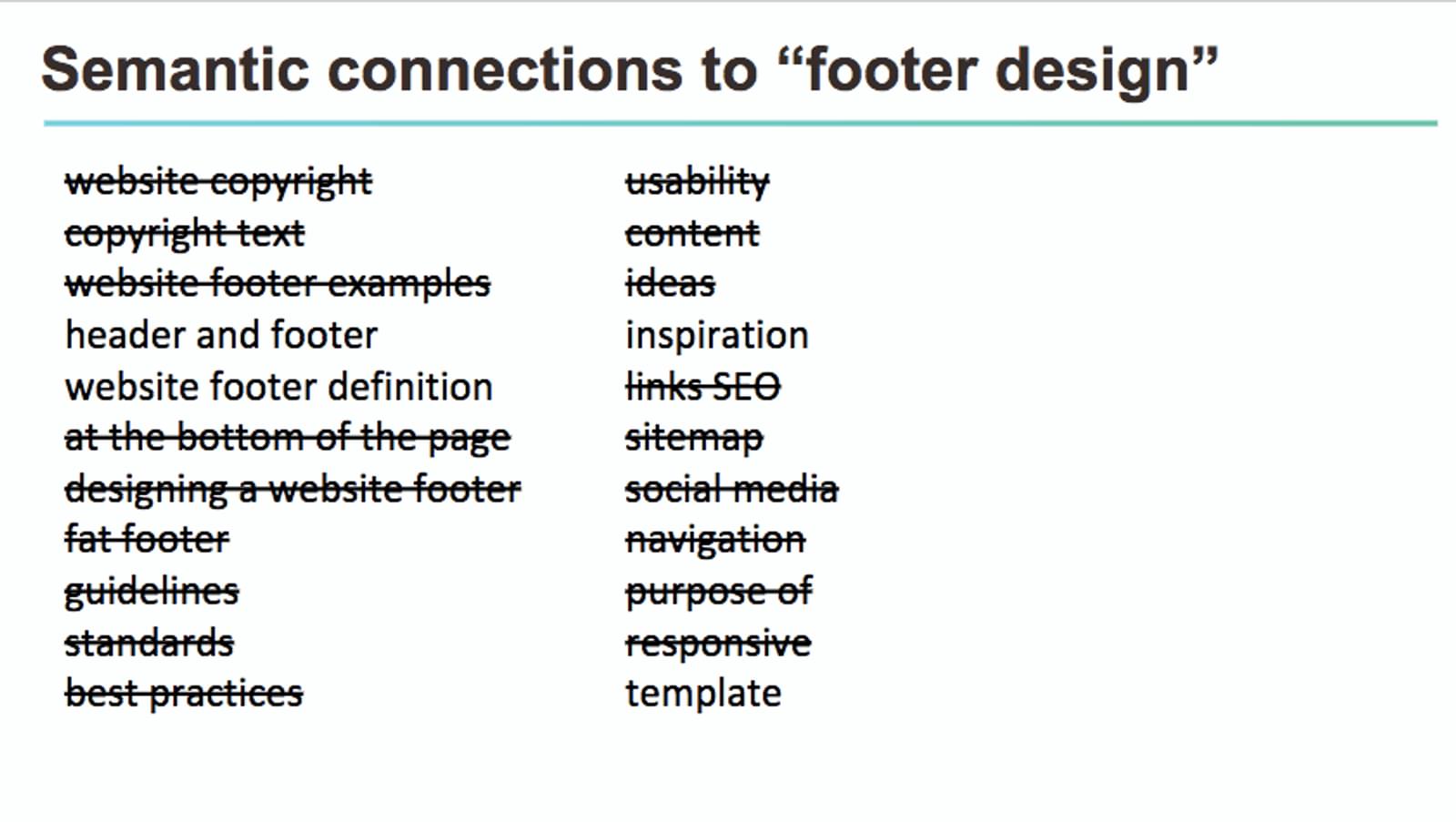
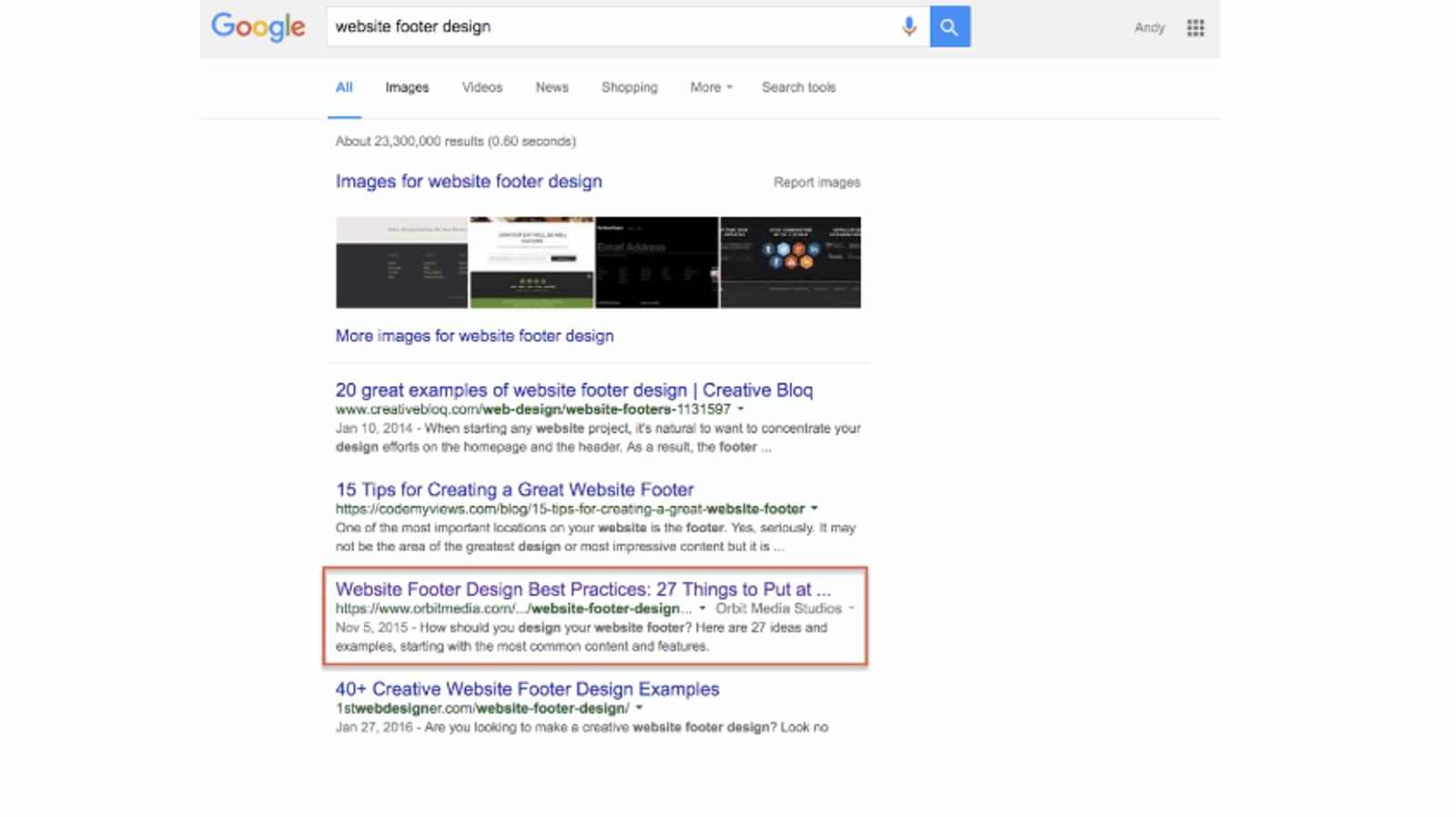
The third search factor: Happiness
- Click through rate from search results pages
- Bounce rate
- Time on page
- Headers, subheads
- Bullet lists, numbered lists
- Bolding and Italics
- Internal links
- Multiple images

- Long content gets shared more
- Long content attracts more links
- Long content correlates with high rankings
- Long content generates more leads
How can knowing about semantic SEO help you in ActiveCampaign?
- They are looking for an answer to a question
- You want to attract the right people to your website
- They are going to leave as soon as they get their answer
- You want to get their contact information and stay in touch
“Message matching” with ActiveCampaign Forms and a welcome series
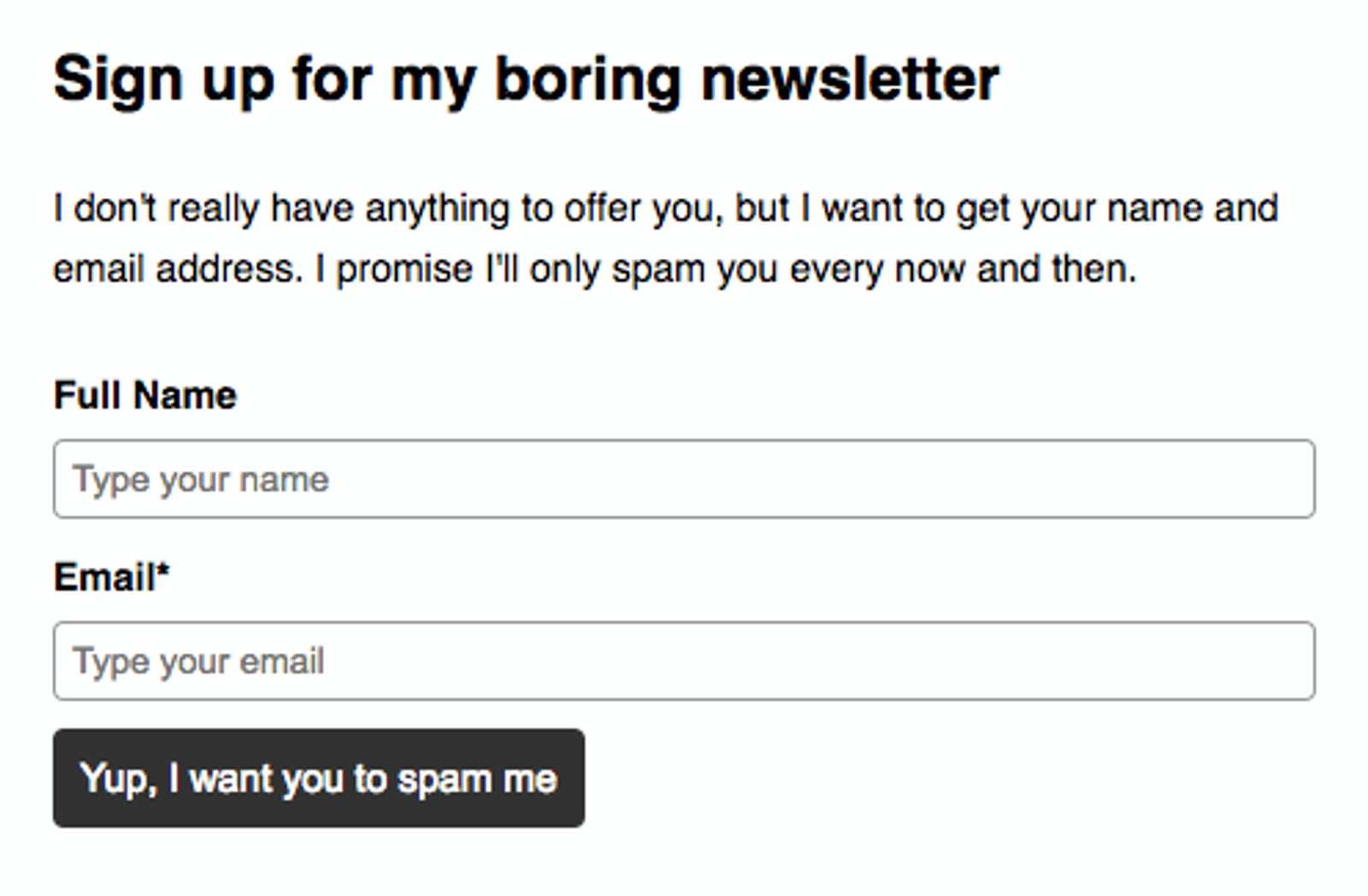
If most newsletter forms were totally honest
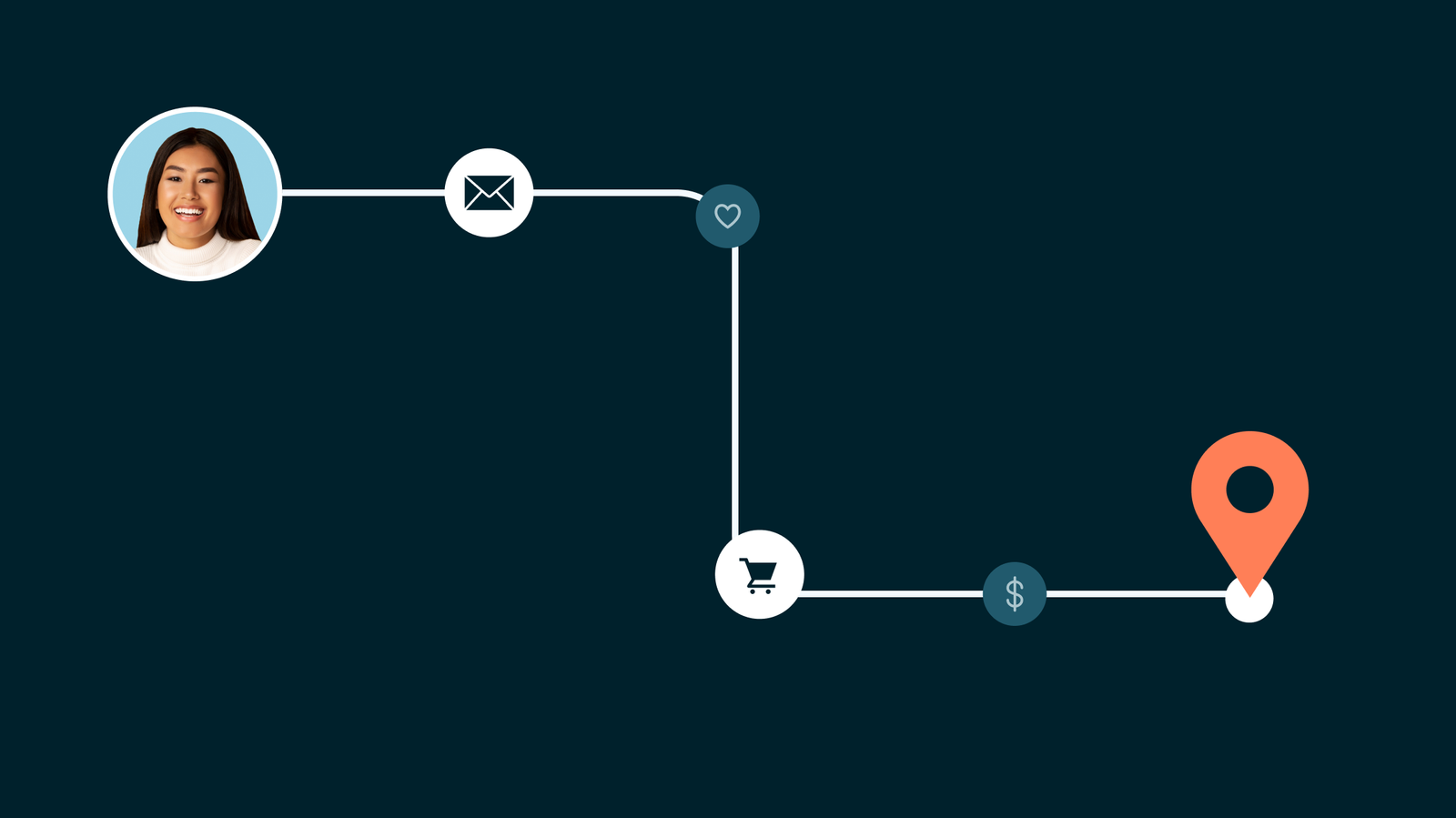
How can you convert more website visitors into contacts (and leads, and customers)?Message matching.Message match your visitor’s “searcher intent”
People who come to you from Google have a specific searcher intent—a specific problem they’re trying to solve.So if you want to convert them into contacts...offer them more stuff related to their problem!You can offer a lead magnet, or just highlight a specific benefit in the copy for your CTA.Once you collect contact information, you can send people through a welcome series that gives them more information on the specific problem they were trying to solve.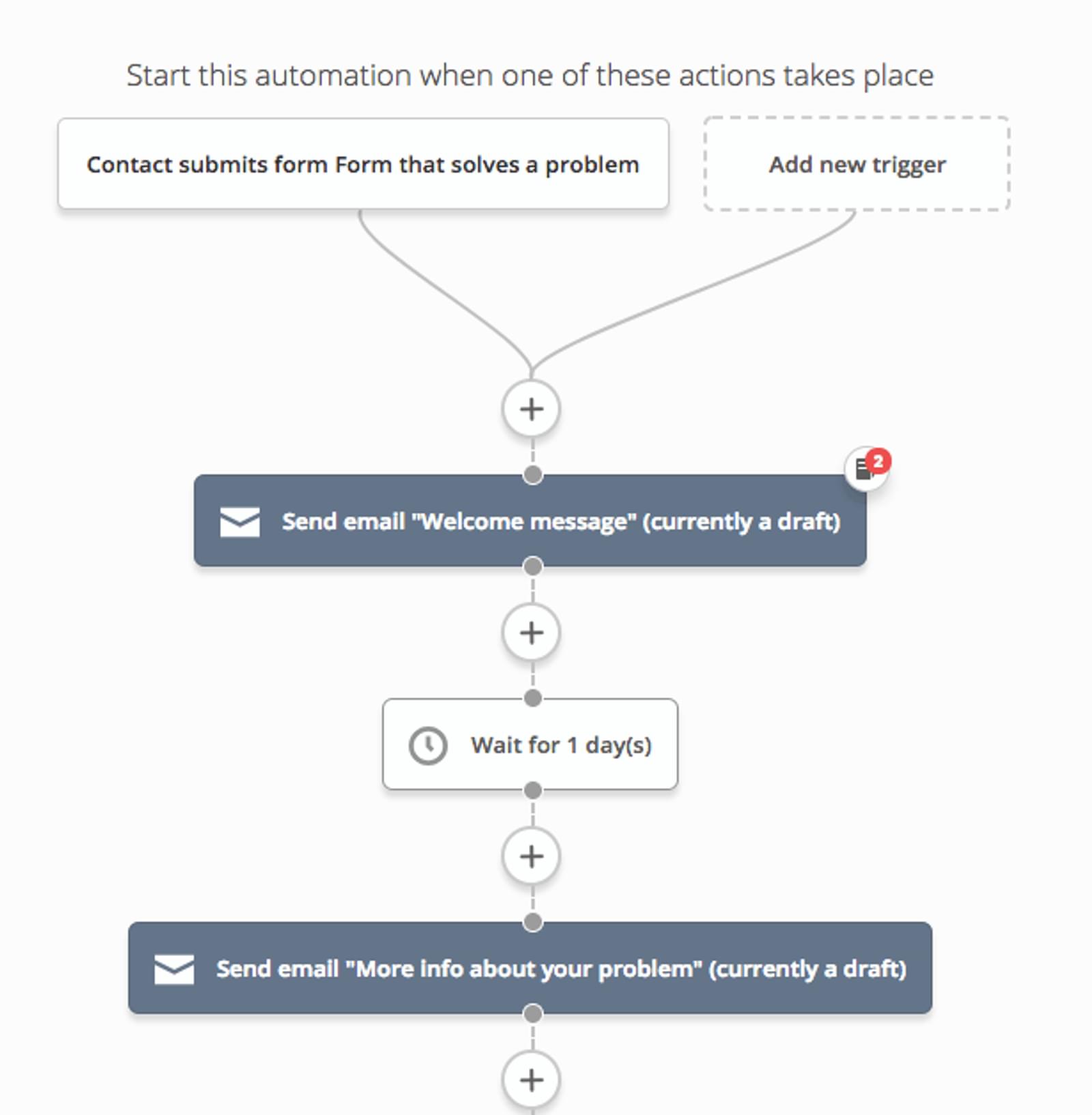
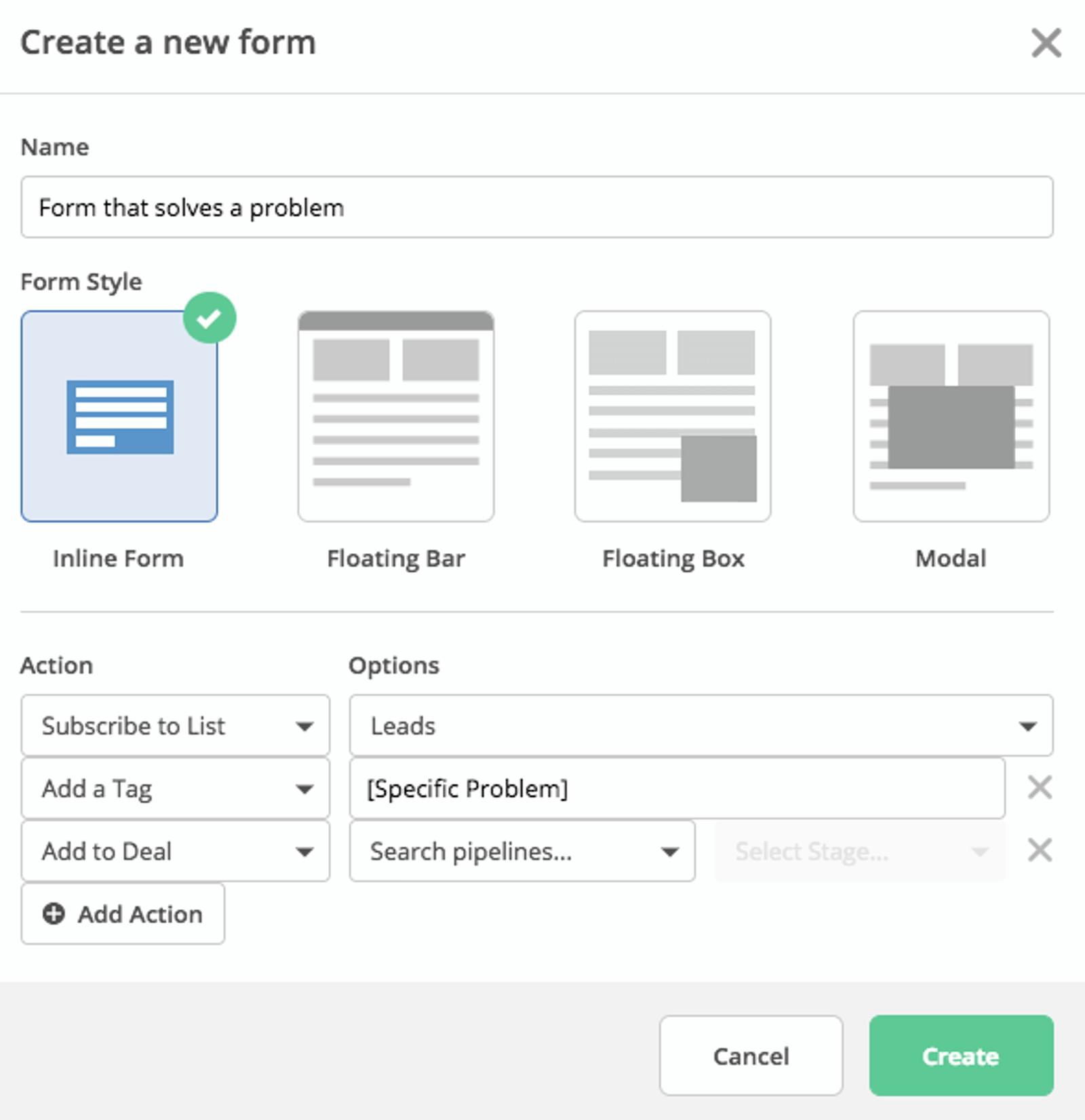
A form that adds people to a list and a deal while segmenting
That means you can create as many different lead magnets and welcome automations as you need.So when someone finds you because you did great semantic SEO, you don’t need to offer them something generic.Instead, you can make a specific offer that’s exactly what they’re looking for.